D-Link ShareCenter Pro storage support RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 1+0 (10), RAID 5 and RAID 6. Each RAID type has its trade-offs in reliability, performance and cost.
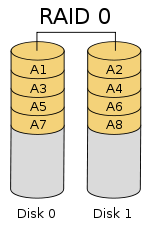
RAID 0 provides the best performance and fastest data transfer speeds. Data is split into blocks that are written (striped) across all the drives in the array. Using multiple disks (at least 2) at the same time, RAID 0 offers superior I/O performance. The disadvantage of RAID 0 is that there is no data protection in the event of a disk drive failure.
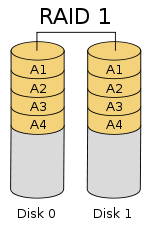
RAID 1 provides data redundancy by mirroring or duplicating the data from one disk to another disk. Data is stored twice by writing to both the data disk (or set of data disks) and a mirror disk (or set of disks) . If a disk fails, the controller uses either the data drive or the mirror drive to recover data and continues operation. At least 2 disks are required for operation. The main disadvantage of RAID 1 is that the effective storage capacity is only half of the total disk capacity because all data gets written twice.
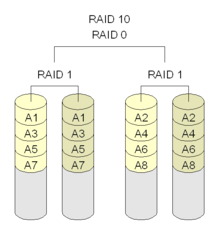
RAID 1 + 0 (also known as RAID 10) combines the advantages of RAID 0 and RAID 1 in a single system. It provides security by mirroring all data on a secondary set of disks while using striping across each set of disks to speed up data transfers.
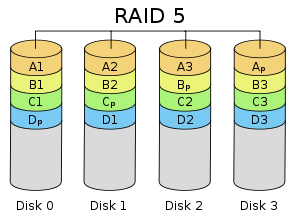
RAID 5 is the most common secure RAID level. It offers data protection and increases throughput by creating data parity and distributing it to all the provided disks. Data is transferred to disks by independent read-write operations. Instead of a dedicated parity disk, parity information is spread across all drives. At least 3 disks are required for operation. A RAID 5 array can withstand a single disk failure without losing data or access to data.
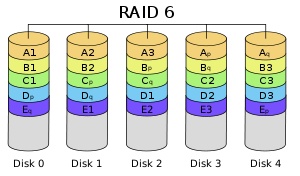
RAID 6 is the slowest performing RAID level because of the overhead associated with the controller's dual parity calculation. RAID 6 is a more efficient method to protect data in the case of a dual drive failure. At least 4 disks are required for operation